Case Studies
Highlights
Benefits
- Improved reliability, availability, and performance
- Safely extend maintenance intervals while controlling asset degradation and failure risk
- Faster troubleshooting, maintenance cost savings, higher operating efficiency
Features
- Insight for planning next maintenance activity
- Advisories for performance and emissions targets
- Coordination of planned outages with maintenance tasks
Applications
- Energy applications including oil and gas, thermal, geothermal, co-generation, solar, hydrogen, and CCUS
- Industrial power generation, mechanical drive, heating and cooling
Overview
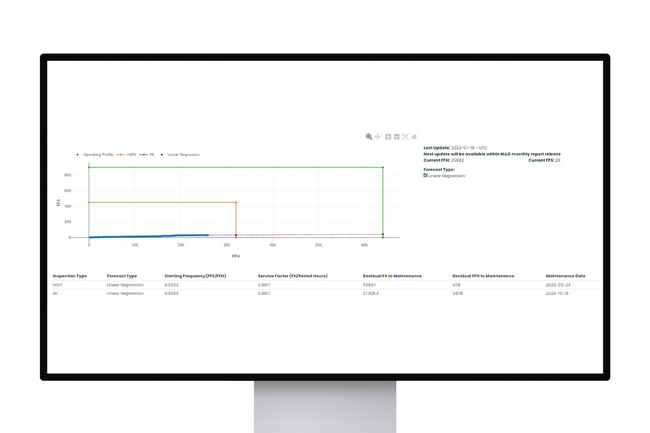
Gas turbine operating profile
- Digital solution provides continuous monitoring of equipment operating profile and calculates the time to next maintenance
- OEM proprietary analytics calculate how assets are consuming their residual life, highlighting if equipment is shifting from hours-based to starts-based or vice versa
- Calculates cumulative counters for fired hours, fired starts, and emergency shutdowns—to forecast dates for next maintenance intervals according to the standard or customized maintenance schedule
Dry low emission (DLE) health status
- Digital solution providing an overview of the health status of the gas turbine’s combustion system, identifying non-optimal behaviors in terms of performance and emissions, with recommendations to operate assets eliminating potentially out-of-spec conditions
- Web application gives 24/7 visibility of combustion data and status

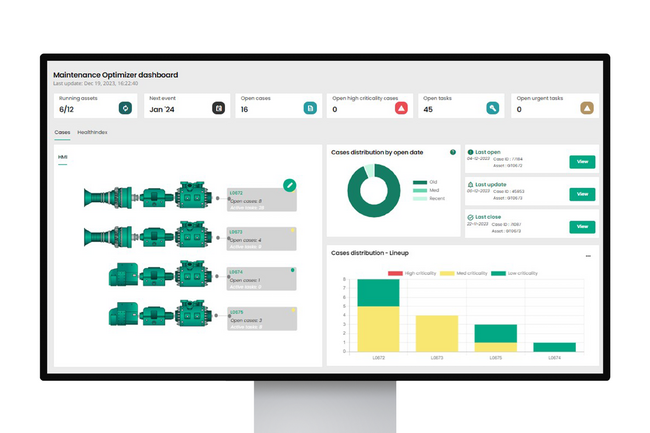
Maintenance optimizer
- Digital service built on physic-based models, remote monitoring data, and degradation models
- Accurate calculations prioritize maintenance tasks by severity, impact, and likelihood
- As an additional feature, Health Index provides an immediate indication of the health status of the monitored equipment, reducing unplanned downtime through early identification of the problems and proactive remediation
- Combine with maintenance flexibility capabilities to safely extend maintenance intervals through asset degradation risk monitoring
- Combine with upgraded hardware and control surveillance systems to achieve de-manned operation
Maintenance flexibility
Condition-based Maintenance (CBM)
CBM optimizes assets maintenance, predicting when maintenance should be performed, and which equipment should be prioritized.
CBM maintenance prediction is based on estimation of equipment residual useful life and risk of failure, calculated by proprietary analytics and expert engineers’ analysis.
Condition based maintenance online allows customers to:
- Switch from fixed-interval planned outages to flexible approach
- Increase unit availability by extending maintenance intervals
- Optimize maintenance scope by focusing only on components with higher risk of failure
Dynamic L1
Dynamic L1 is a digital service performing a condition-based maintenance strategy for aeroderivative gas turbines. It includes software, hardware, upgrades, engineering advisory services, and leverages the extensive domain knowledge and remote connectivity at the Baker Hughes iCenters™, which monitor over 1,600 critical rotating machines worldwide and covers over 60 LNG projects currently in operation. It is designed to extend the turbine inspection interval from 4,000 to 17,500 fired hours—or from six months to approximately two years.










