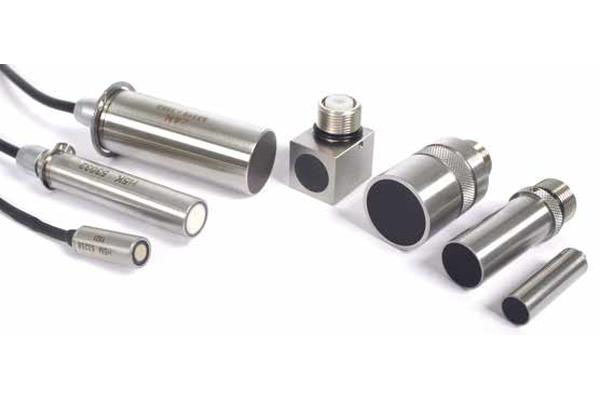
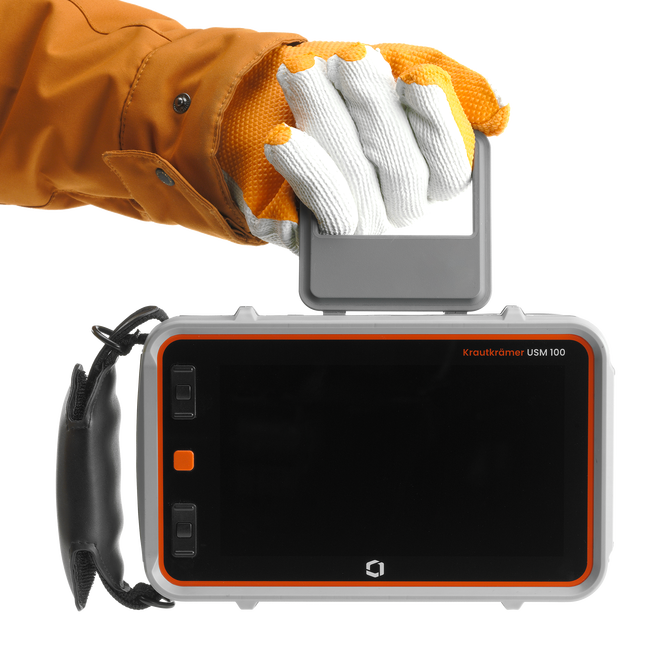
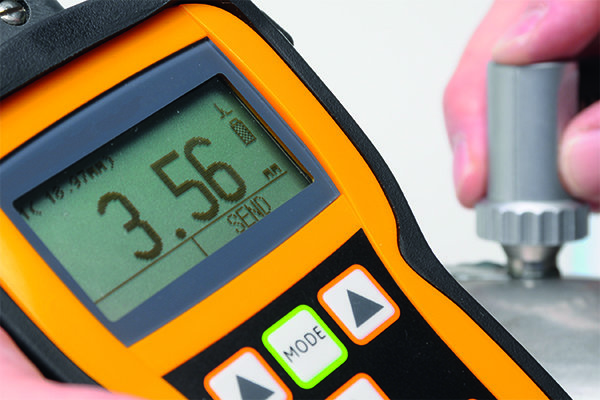
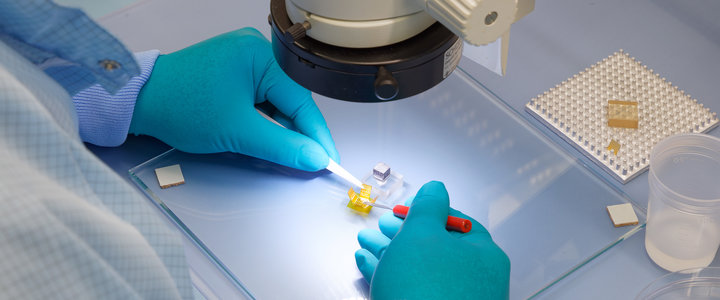
NDT ultrasonic testing product range from Waygate Technologies
Waygate Technologies' industrial ultrasonic testing equipment (UT) combines decades of expertise with cutting-edge innovation to deliver precise, non-destructive testing solutions. Built on the Krautkrämer legacy, our advanced UT tools are designed to detect even the smallest flaws in materials like metals, plastics, and composites, ensuring the highest level of protection for your critical assets.
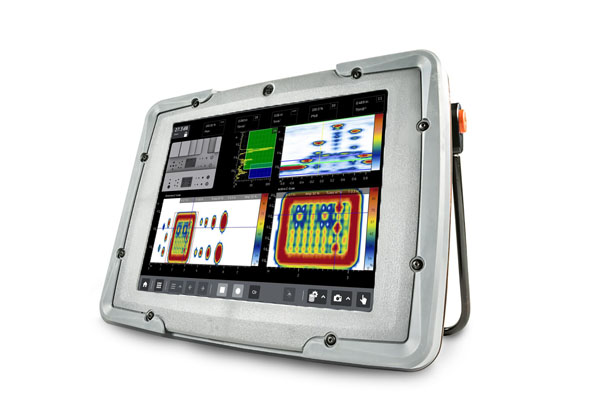
Our technology integrates powerful features such as phased array systems and automated inspection software, enabling you to perform accurate and efficient inspections with confidence. Whether you’re dealing with routine maintenance or challenging inspection scenarios, our equipment helps minimize downtime and maintain productivity.
If you’re facing an urgent or complex inspection challenge that can't be met with off-the-shelf solutions, our AppLab Service offers tailored, expert-driven solutions. Leveraging our deep industry expertise, we develop custom approaches to meet your specific needs, ensuring your ultrasonic testing processes are optimized for success.
Industrial ultrasonic testing that meets your needs
When it comes to safeguarding your most valuable assets, precision and reliability in non-destructive testing (NDT) are essential. Waygate Technologies offers advanced ultrasonic testing (UT) solutions that are trusted across industries for their ability to detect even the smallest flaws in critical materials like metals, plastics, and composites.
Advanced Flaw Detection
Our industrial ultrasonic testing equipment is designed with cutting-edge technology to ensure that every inspection is accurate and thorough. Whether you're assessing welds, forgings, or tubing, our UT tools provide the detailed insights needed to maintain safety and operational integrity. Built on the legacy of Krautkrämer, these solutions deliver superior performance, allowing you to identify potential issues before they escalate.
Efficiency That Reduces Downtime
Downtime can be costly and disruptive. That’s why our UT solutions are engineered for efficiency, helping you quickly locate and address faults to keep your operations running smoothly. With intuitive interfaces, portable designs, and advanced software, our equipment makes it easier to perform thorough inspections in less time, minimizing interruptions to your workflow.
Tailored Solutions for Unique Challenges
Not all inspection challenges can be met with standard equipment. For those times when off-the-shelf solutions fall short, our AppLab Service offers custom-designed approaches. Leveraging decades of NDT expertise, our team works closely with you to develop solutions tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that even the most complex inspection tasks are handled with precision and reliability.
Discover Our Diverse Family of Ultrasonic Inspection Solutions:
Where ultrasonic testing (NDT) matters

Automotive
Inspection & NDT solutions for the automotive industry
Why choose Waygate Technologies
At Waygate Technologies, we are committed to excellence in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT). Our long-standing history and expertise, combined with cutting-edge innovation and dedicated customer support, make us the trusted choice for industries worldwide.
- Over 120 Years of Experience: With a deep-rooted history in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT), Waygate Technologies has over a century of experience in delivering reliable, high-quality inspection solutions across multiple industries.
- Building on 75 Years of The Krautkrämer Legacy: Our UT products are built on the pioneering work of Krautkrämer, a name synonymous with innovation in ultrasonic testing. For 75 years, Krautkrämer products have set the standard for precision and reliability in industrial inspection.
- Tailored Solutions for Complex Challenges: Our AppLab Service offers customized, expert-driven solutions for your most challenging inspection needs, ensuring that no problem is too complex to solve.
- Comprehensive Global Support: We provide world-class customer service, including preventive maintenance, expert training, and global technical assistance, ensuring your operations run smoothly and efficiently, no matter where you are.
Our product success stories
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a form of non-destructive testing (NDT) that employs high-frequency sound waves for the purpose of characterizing the thickness or internal structure of a given sample. The frequencies used for UT are typically in the range of 500 kHz to 20 Mhz.
As a non-destructive testing method, ultrasonic testing is ideally suited to the detection of flaws, defects, and welded seams where destruction of the target sample is not an option.
In addition to detecting flaws in production samples, periodic UT inspections are also perfect for checking for corrosion in existing equipment, such as pipelines, and is therefore an indispensable part of any predictive maintenance program.

Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is ideally suited for the inspection of material structures such as metals, ceramics, plastics, and composites.
While denser materials up to and including concrete can be successfully inspected, the output resolution is usually less-defined.
Highly porous biological materials such as wood and paper do not react well to ultrasonic testing.

Yes, ultrasonic testing (UT) can be used on stainless steel. UT is a non-destructive testing method that uses high-frequency sound waves to detect flaws or measure thickness in materials. While stainless steel can present some challenges due to its grain structure, UT is still an effective method when performed correctly, often using specific techniques to address potential difficulties with signal scattering.

Ultrasonic testing (UT) works by sending high-frequency sound waves into a material using a transducer. These sound waves travel through the material and reflect back to the transducer when they encounter a boundary or defect, such as cracks or voids. The reflected waves are then recorded and analyzed to determine the location, size, and nature of the flaw. By interpreting the time it takes for the waves to return and the strength of the reflection, inspectors can assess the material's integrity without causing any damage.

Selecting the right angle probe in ultrasonic testing depends on several factors, including the material being inspected, the type of defect you're trying to detect, and the geometry of the part. Here's a basic guide to selecting an angle probe:
- Material Type: Different materials will affect sound wave transmission. Choose a probe with a frequency that matches the acoustic properties of the material.
- Defect Location and Type: For surface or near-surface flaws, a shallower angle (e.g., 45°) is often used. For deeper defects, higher angles (e.g., 60° or 70°) may be more effective.
- Part Geometry: Complex geometries may require specific angles to ensure proper coverage of the inspection area. For example, 45° is commonly used for weld inspections, while other angles might be required for specific shapes.
- Code and Standards: Follow industry-specific standards (e.g., AWS, ASME) which may dictate specific probe angles for particular inspection types.
Proper probe selection ensures accurate detection of defects and reliable test results.

To test an ultrasonic transducer, follow these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the transducer for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or wear on the surface. Ensure that the cables and connectors are intact.
- Impedance Testing: Use an impedance analyzer to measure the electrical impedance of the transducer. Compare the result with the manufacturer's specifications to ensure it falls within the acceptable range.
- Pulse-Echo Test: Connect the transducer to an ultrasonic testing device and perform a pulse-echo test. Place the transducer on a known calibration block and observe the reflected signal on the screen. Ensure that the signal is clear and has the correct amplitude and timing.
- Frequency Check: Verify that the transducer is operating at the correct frequency using an oscilloscope or frequency analyzer. This ensures the transducer is emitting sound waves at the specified frequency.
- Signal Strength and Consistency: Check the strength and consistency of the signals produced by the transducer over multiple tests. A weak or inconsistent signal may indicate that the transducer is malfunctioning.
These tests help ensure that the ultrasonic transducer is functioning properly and providing accurate results.

The three main types of ultrasonic inspection methods are:
- Pulse-Echo Testing: This method sends a pulse of sound waves into the material, and the waves reflect back when they hit a flaw or boundary. The time it takes for the echo to return is used to determine the location and size of defects. It's widely used for detecting internal flaws and measuring thickness.
- Through-Transmission Testing: In this method, two transducers are used—one on each side of the material. One transducer sends sound waves through the material, while the other receives them on the opposite side. A reduction in signal strength indicates the presence of a flaw. This method is effective for detecting large defects.
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT): This advanced technique uses multiple transducer elements that can be controlled to steer, focus, and scan sound beams across a material. PAUT provides detailed, real-time images of the internal structure, allowing for more accurate detection and sizing of defects.
These methods are used based on the specific inspection requirements and material properties.
Other services

Industrial radiography and CT

NDT software
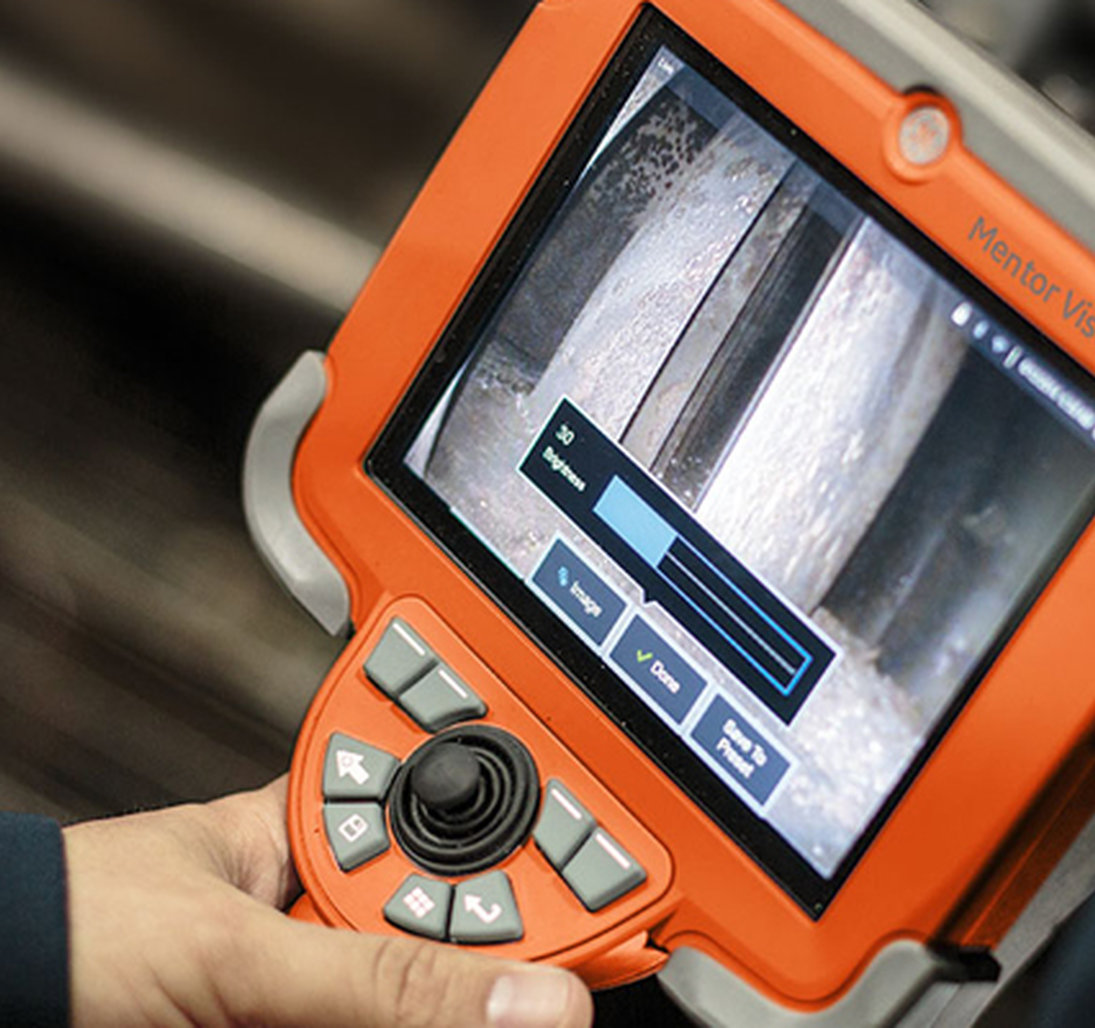

Remote visual inspection

Video borescopes